Friday, February 13, 2015
MySQL installation in remote Ubuntu 12 04 server using PuTTY and accessing 3306 port in local mysql client by Tunneling
In this post you will learn how you can install MySQL in remote Ubuntu server as well how you can access the installed database from server to your local machine using PuTTY Tunneling.
Environment:
Client location
1) Ubuntu Server 12.04
Development location
1) Windows 7 64 bit OS ( DEV location)
2) PuTTY installed in Windows.
3) DBVisulalizer(OR any MySQL client tool installed for connecting to remote servers)
4) MySQL installed in Windows and service running state.
This post is divided into two sections.
PART-I : MySQL installation in remote Ubuntu 12.04 Server using PuTTY
PART-II : How to by pass 3306 port number by Tunneling concept to access the MySQL database.
( Even though if 3306 port number is not opened in the Ubuntu server we can access the mySQL database)
Connect to Ubuntu server using given credentials(Username, password and ppk file)
PART-I : MySQL installation in remote Ubuntu 12.04 Server using PuTTY
1)root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167: aptitude update
2) Download and install using below command
root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167:aptitude install mysql-server
3) The installer should ask you to set a root password : set it as "password" and click on OK.
4) Installation will complete after clicking on OK.
5) MySQL Service status command after installation completed
root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167:/# service mysql status
mysql start/running, process 28645
6) MySQL Start command :
root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167:/# service mysql start
mysql start/running, process 29040
7) MySQL Stop command:
root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167:/# service mysql stop
mysql stop/waiting
8) MySQL installed location:
root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167:/# which mysql
/usr/bin/mysql
9) Connect to MySQL
root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167:/# /usr/bin/mysql -u root -p
Enter password:password
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 36
Server version: 5.5.34-0ubuntu0.12.04.1 (Ubuntu)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type help; or h for help. Type c to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
10) Find mySQL version using below command
mysql>SHOW VARIABLES LIKE "%version%";
PART-II : How to by pass 3306 port number by Tunneling concept to access the MySQL database
1. On your PuTTY window which will drop down the options in a list shown in below figure.
(Assume that you have already working with PuTTY for MySQL installation and not closed it).
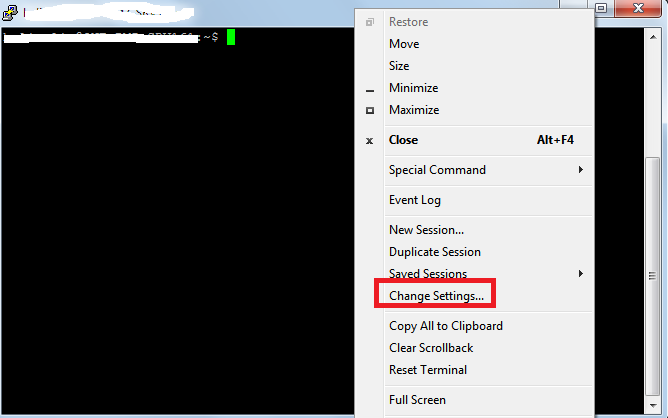 2. Click on Change Settings
2. Click on Change Settings
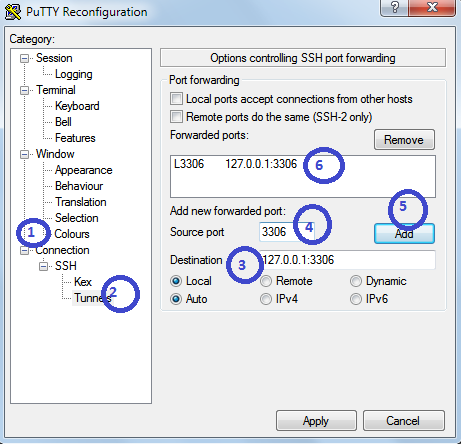
i) On the left side click on "Connections"
ii) Expand SSH then click on Tunnels
iii) Give destination as : 127.0.0.1:3306 or localhost:3306
iv) Give source port as : 3306
v) Now, click on Add
Find OS version
Find which Ubuntu version number using this command
root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167:/usr/bin# cat /etc/*-release
DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu
DISTRIB_RELEASE=12.04
DISTRIB_CODENAME=precise
DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Ubuntu 12.04.3 LTS"
NAME="Ubuntu"
VERSION="12.04.3 LTS, Precise Pangolin"
ID=ubuntu
ID_LIKE=debian
PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu precise (12.04.3 LTS)"
VERSION_ID="12.04"
Environment:
Client location
1) Ubuntu Server 12.04
Development location
1) Windows 7 64 bit OS ( DEV location)
2) PuTTY installed in Windows.
3) DBVisulalizer(OR any MySQL client tool installed for connecting to remote servers)
4) MySQL installed in Windows and service running state.
This post is divided into two sections.
PART-I : MySQL installation in remote Ubuntu 12.04 Server using PuTTY
PART-II : How to by pass 3306 port number by Tunneling concept to access the MySQL database.
( Even though if 3306 port number is not opened in the Ubuntu server we can access the mySQL database)
Connect to Ubuntu server using given credentials(Username, password and ppk file)
PART-I : MySQL installation in remote Ubuntu 12.04 Server using PuTTY
1)root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167: aptitude update
2) Download and install using below command
root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167:aptitude install mysql-server
3) The installer should ask you to set a root password : set it as "password" and click on OK.
4) Installation will complete after clicking on OK.
5) MySQL Service status command after installation completed
root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167:/# service mysql status
mysql start/running, process 28645
6) MySQL Start command :
root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167:/# service mysql start
mysql start/running, process 29040
7) MySQL Stop command:
root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167:/# service mysql stop
mysql stop/waiting
8) MySQL installed location:
root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167:/# which mysql
/usr/bin/mysql
9) Connect to MySQL
root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167:/# /usr/bin/mysql -u root -p
Enter password:password
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 36
Server version: 5.5.34-0ubuntu0.12.04.1 (Ubuntu)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type help; or h for help. Type c to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
10) Find mySQL version using below command
mysql>SHOW VARIABLES LIKE "%version%";
PART-II : How to by pass 3306 port number by Tunneling concept to access the MySQL database
1. On your PuTTY window which will drop down the options in a list shown in below figure.
(Assume that you have already working with PuTTY for MySQL installation and not closed it).

i) On the left side click on "Connections"
ii) Expand SSH then click on Tunnels
iii) Give destination as : 127.0.0.1:3306 or localhost:3306
iv) Give source port as : 3306
v) Now, click on Add

3. Once you click on Add you should find added host in the box.
4. Impotently note that in your local machine(Windows) MySQL server is running.
In Destination you are giving localhost or 127.0.0.1 so you should run MySQL server in your local machine. And note that from the PuTTY(lets say Ubuntu server) you are by passing 3306 port number to get the actual MySQL database installed on the Ubuntu server.
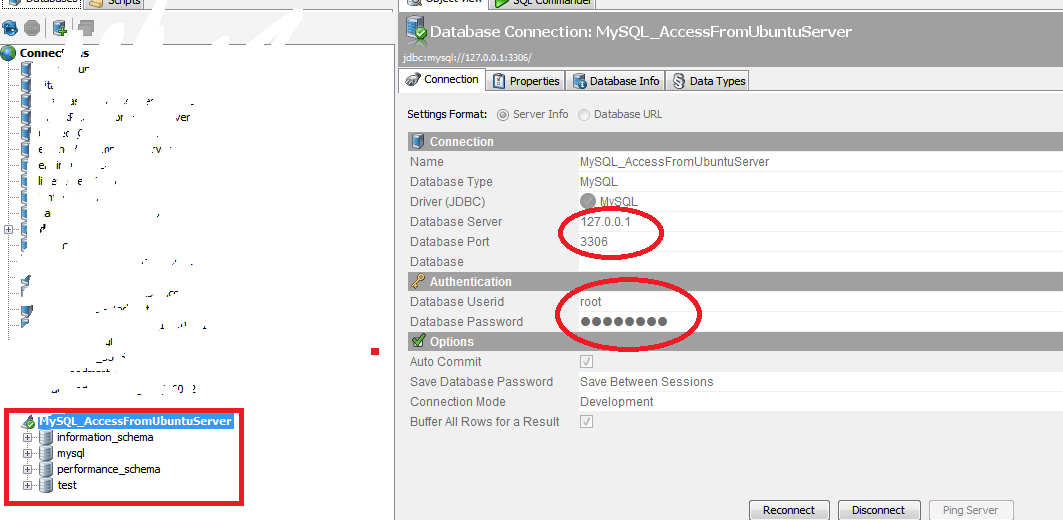
5. Now test whether it is working or not.
Open MySQL Query browser or any client tool where you can access remote MySQL server.
In this example I have taken DBVisualizer

Give all the database deatils
Database server : 127.0.0.1 or localhost (remember that it is not the IP of Ubuntu server).
Database Port : 3306
Username and password : root/password
Find OS version
Find which Ubuntu version number using this command
root@SAD-AKAR-LLM167:/usr/bin# cat /etc/*-release
DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu
DISTRIB_RELEASE=12.04
DISTRIB_CODENAME=precise
DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Ubuntu 12.04.3 LTS"
NAME="Ubuntu"
VERSION="12.04.3 LTS, Precise Pangolin"
ID=ubuntu
ID_LIKE=debian
PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu precise (12.04.3 LTS)"
VERSION_ID="12.04"
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.